Bone Grafting
Correcting & Repairing Gums
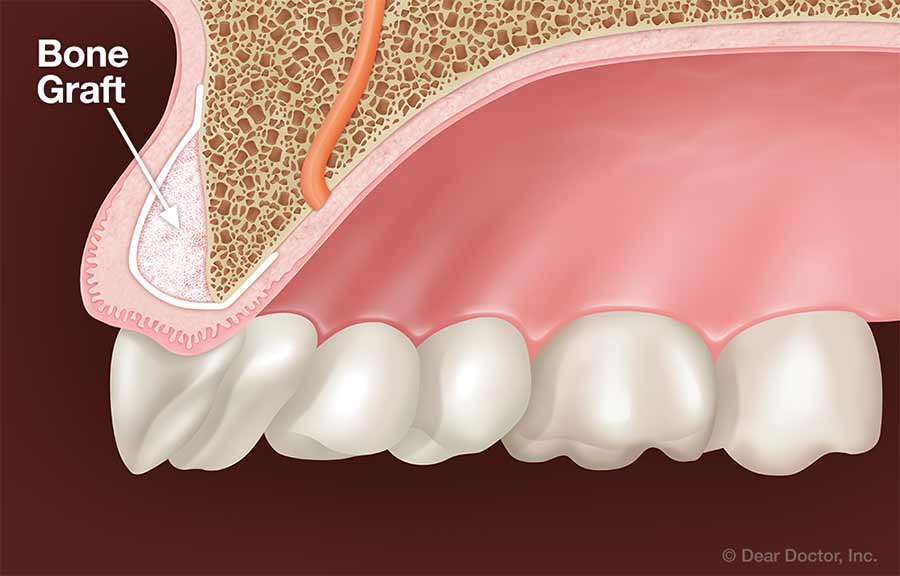
Bone grafting (hard tissue augmentation) is an important tool to be used in specific clinical situations. In some cases, deficiencies in the jawbone can be created by previous infections, trauma or developmental deficiencies. This may prevent the proper placement of dental implants. Bone grafting allows us to repair these defects and in many cases can be performed at the same time as implant placement and therefore not requiring additional procedures. In some cases however, a separate procedure is needed based on the severity of the deficiency. Donor material is typically used, thus eliminating the need for harvesting bone from the patient, significantly reducing discomfort and facilitating recovery.
Bone grafting may also be employed in the treatment of periodontal disease. During a periodontal surgical procedure, Dr. Leja may opt to add a small amount of bone adjacent to a tooth or implant in order to repair a defect caused by periodontal disease.
Types of Bone Grafts
-
- Autograft: a bone graft using your own bone, usually sourced from the hip bone or back of the jaw.
- Allograft: a bone graft using bone sourced from a human donor.
- Xenograft: a bone graft using bone from an animal, usually a cow.
- Alloplast: a bone graft using synthetic material containing calcium, phosphorous and hydroxylapatite
